How to Develop an Enterprise Web Application?
Developing large-scale systems brings its own challenges – from defining the stages of development to implementing scalability and global content delivery. With the right framework, architecture, and development approach, enterprises can overcome these obstacles and build resilient, user-centric solutions.
The guide provides insights into:
- Key pillars of successful enterprise web app development
- Cost factors influencing enterprise web projects
- Choosing the right tech stack, framework, lifecycle model, and development process
- Security best practices and modern authentication methods

Table of Contents
The modern economy is going more and more digital. New devices and platforms emerge with the speed of light. However, web browsers are here to remain among the popular touchpoints between your business and customers.
But, the stakes in enterprise web application development today are high. Your product should satisfy hundreds of thousands of separate requirements. There’s a host of unique user requirements you need to meet. So where do you begin?
In this guide, we’d like to outline all the essential prep stages and key decisions you’ll need to make as you get started with an enterprise web application development project.
Table of Contents
The Pillars of Successful Enterprise Web Application Development Strategy
Successful and effective enterprise-level web applications share several defining characteristics:
- They automate and/or eliminate routine processes;
- They provide clear value to the end-user;
- And they are agile, secure, and fast.
The easiest way to arrive with a product that is both effective and intuitive is to define your end goals first. What business outcomes do you plan to achieve? Are there any KPIs to measure those?
Create a list of exact processes your software should be able to accomplish; routines it should help you get rid of and the exact set of functions it should perform. Involve multiple stakeholders in the discussion process and gather feedback from different groups of end-users.
Next, you can formalize those needs and preferences within a list of requirements that you’ll send to potential vendors during the request for proposal stage.
The Right Web Applications Lifecycle Model
The web application lifecycle stands for the step-by-step process of developing a custom web application.
Each web development company sets forth its unique style of operations for developing, testing and deploying apps. In our case, we vouch for an Agile approach to software development.
There are several advantages of an Agile approach:
- Reduces the number of project management processes;
- A stronger focus on collaboration and efficient teamwork;
- Automates the max amount of processes without compromising the quality;
- Allows remaining flexible to changes that may occur during the development project.
Strong Web Application Development Process
This serves as a backbone for ensuring that your product will be delivered on time, up-to-specs and without any flows.
Here’s how a web application development process looks at our company:
- Development of roadmap documentation – defining web application, purpose, goals, and direction;
- Audience/user research;
- The creation of functional product specifications or feature summary documents;
- Technology selection, settling on technical specifications of the product;
- Third-party integration analysis and selection;
- Web application visual guide, design layout and wireframing;
- Entering database structure design and application development;
- Quality assurance and testing;
- Maintenance and further tech support (if required).
An Appropriate Web Application Framework
Web application frameworks stand for a set of program libraries, tools, and components organized in an architecture system, which allows programmers to build and maintain complex enterprise web application projects using a more efficient approach.
Using an appropriate web application framework for an enterprise web development project is crucial. Without doing so, you risk extending the development timeline and compromising the code quality. In development we choose frameworks that will ensure your web app can scale efficiently to support high-traffic scenarios without performance degradation.
Advantages of using web application frameworks are:
- Program actions and logic are separated from CSS and design files, meaning your website design goes smoother as our professionals can edit the interface and implement changes without additional help from an engineer.
- Each build is based on the module, libraries, and tools, which allows developers to share libraries and implement complex features in a faster, more efficient pace.
- The end code is of higher standards, more consistent and requires less testing afterward.
- A framework eliminates several security risks as those are addressed when the framework is being built.
- Web frameworks simplify the process of building different integrations in a fast and secure manner.
Responsive and Adaptive Web Interfaces
Responsive and adaptive web design is a must for modern enterprise applications.
In a nutshell, the two concepts serve the same purpose – deliver excellent UX on different types of devices (PC, laptop, tablet, smartphone, etc). However, there are some important differences between responsive and adaptive web apps.
Based on the user’s device, a responsive website adjusts the placement of design elements and overall layout for the optimal interactive experience. It consists of three key elements:
- A fluid layout
- Responsive images
- Media queries
Adaptive web design supports multiple fixed layout sizes. In this case, the website adapts the size of all elements based on the screen size. In most cases, such designs support the 6 most common screen sizes 320, 480, 760, 960, 1200, and 1600 pixels.
Progressive web apps (PWAs) are a newer trend around town that a lot of market leaders have embraced. These are developed with progressive enhancement as a core tenet, so that they can deliver an app-like experience for any user, regardless of their device and browser choice. PWAs attempt to closely mimic the effect of a native application and they are designed to work offline or with poor connectivity.
How Much Does It Cost to Develop an Enterprise Web Application
In general, depending on the complexity of your end product and company location the standard developers’ rates range is $100 – $149 per hour for nearshore outsourcing (Canada, The UK, and US market on average); $30-$99 per hour if outsourcing to Eastern European markets (Ukraine, Poland, Romania) and under $25 if you choose a low-budget enterprise web development company from India, Vietnam or China (but the quality of work would be respective).
In most cases, the final price quote will also include the costs of website design, UI/UX and wireframing, quality assurance services, and ongoing application tech support and maintenance, etc.
Alternatively, instead of outsourcing the entire project to a vendor, you can opt to hire a dedicated development team that will complement your in-house expertise and work exclusively on your project.
To get an accurate cost estimation from a mid-sized, experienced company that delivers reliable, high-quality, yet cost-effective software solutions, contact the Romexsoft team. We’ll analyze your project requirements and provide a clear, realistic quote tailored to your goals.
Now let’s move to the core essentials of enterprise app development.
Technology Stack for Developing Enterprise Web Applications
Your web application development project will require two types of expertise:
Client-side Coding
Front-end development – the type of code that will power up your website and will be interpreted by web browsers. In fact, any website visitor can view it by enabling the appropriate feature in their browser.
Specifically, you’ll need developers who are proficient in:
- Hypertext Markup Language (HTML5 is the latest version) and Cascading Style Sheets (CSS). As well, Bootstrap 3 is a handy framework our developers use to speed up and streamline web development.
- JavaScript (JS) a
- Front end web frameworks such as Angular, Vue.js, and React.
nd JavaScript libraries such as jQuery.
Server-side Coding
Back-end development – this type of code is interpreted and executed by the webserver. In layman terms, it’s the tech engine, powering all the functions of your web app.
Our company always suggests using Java for enterprise application development projects as it is the most robust, versatile, and stable technology.
Some of the best Java EE (Enterprise Edition) frameworks to use for web development are as follows:
- Spring including Spring Boot and Spring Cloud.
- Hibernate – an excellent ORM framework for building databases.
- Apache Struts2 – an open-source MVC framework for Java.
To build enterprise-grade databases, we recommend using either of the following technologies:
- MySQL
- PostgreSQL
- MSSQL
- Redis
- MongoDB
Finally, if you plan to run your application in the cloud opt for AWS (Amazon Web Services). Firstly, Amazon offers unbeatable levels of availability and can provide the smooth global delivery to ensure maximum uptime. They invest in the latest hardware and infrastructure for their data centers to ensure 99.99% SLAs and minimal network latency.
Secondly, Amazon provides over 200 cloud services across computing, databases, analytics, storage, security, networking, machine learning and AI, mobile and enterprise applications verticals. So it’s unlikely that your enterprise will be forced to compromise on certain functionality.
Lastly, the general benefits of cloud adoption are rather attractive:
- Lower CAPEX/OPEX costs
- Flexible pricing and enterprise discounts
- On-demand scaling and resources provisioning
- Improved disaster recovery
- Business continuity
Feeling confused about your options? Our team would be delighted to advise you on the best tech stack for your enterprise web application or walk you through all the AWS details.
Enterprise Web App Security Best Practices
Cybercrime is on the rise and enterprises are a desired target for malicious actors. However, as a recent series of high-profile breaches have proved, most enterprise web applications still do not comply with the common security standards and contain serious vulnerabilities.
A CyCognito study of 500,000 internet-exposed assets found 52% of cloud assets and 66% of non-cloud assets lacked web application firewall protection. In other words, most enterprise web applications suffer from notorious, yet easily preventable security vulnerabilities. In most cases, those stem from outdated legacy IT, the prevalence of shadow IT practices and abandonment of certain IT assets (that can be exploited by malicious third-parties to access live systems).
Don’t repeat the same mistakes when building a new enterprise web application.
Our company has created a set of guidelines we use to build-in bulletproof security into each of our products. Here are some of the standards we adhere to:
Test Inputs Rigorously
Your website code opens a potential path into your internal systems and sensitive customer data. If your software pulls any kind of data from the Internet, inevitably someone will try to sneak past your security and cause havoc.
Here’s a classic example of how SQL injections happen. A web form on your enterprise website may simply ask the user to type their ZIP code, then those characters are turned into an SQL query. Yet savvy hackers can add extra characters that expand the scope to be more than a simple search. When your software grabs all the input data, it ends up feeding the SQL directly to the database and your system gets infected.
Thus, always make sure that the company you work with takes code review and testing very seriously. Yes, the QA process can be time-consuming, but programmers should check (and double-check!) their code vigorously. That’s exactly why we practice peer-to-peer code reviews in our company – this way a different programmer can take a fresh look at the code, review and vet it with higher accuracy.
Additionally, we recommend using DALs to prevent SQL injections. Adding an abstraction layer over your databases will make the majority of SQL injections fail. However, this option can be a bit expensive in development, as every single database call will require modifications and interpolations at the DAL layer. At our company, we standardly use Hibernate Framework.
Opt for Passwordless Authentication Methods
Passwords are long overdue for innovation. They no longer serve the purpose of protecting critical app data well enough. Microsoft states that passkey sign-ins have around 98% success rate vs 32% for traditional passwords, and new accounts are being made “passwordless by default.”
The most viable alternative options for enterprises are as follows:
- Enable N-factor authentication and OTP passwords for authenticating critical in-app actions and/or accessing certain functionality. However, this poses additional difficulties from the end-users perspective.
- Using Security Assertion Markup Language (SAML) can be a better option for authenticating users securely through a 3rd party identity provider.
- On top of SAML, enforce MFA for high-risk or critical access (which can push notification and hardware token) – this covers critical in-app actions as you noted.
- Fast Identity Online (FIDO) protocol is worth the consideration too, especially if you plan to incorporate biometrics authentication too.
Use a Web Application Firewalls
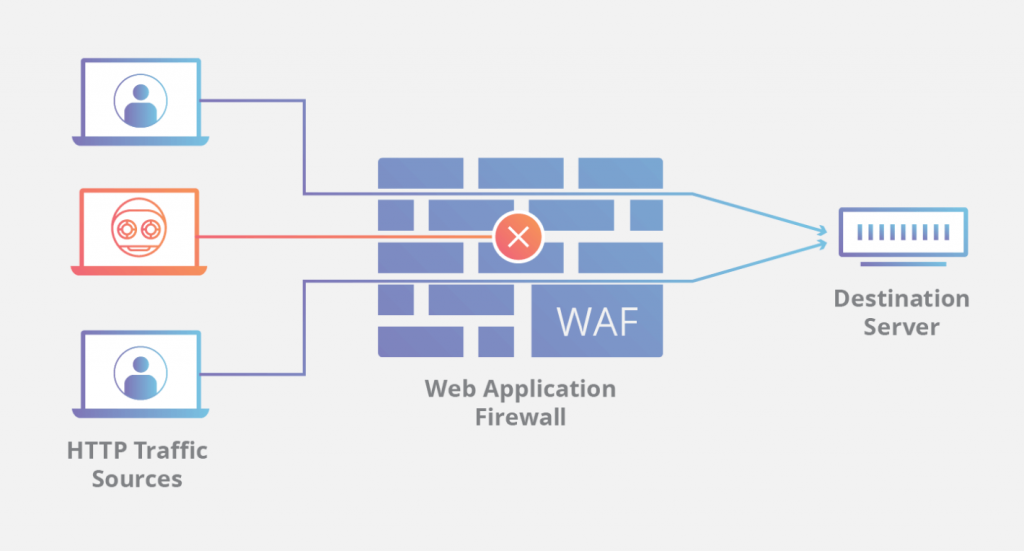
Source: Cloudflare
A Web Application Firewall (WAF) acts as a middleware ‘shield’ between your enterprise web application and all the Internet traffic. It’s a common security mechanism for safeguarding your apps for the following cyber attacks:
- SQL injections
- Cross-site forgery
- File inclusion
- Cross-site-scripting (XSS)
- DDoS attacks
The goal of a web application firewall is to capture harmful web traffic that other security mechanisms may have missed and prevent it from reaching your web servers. Depending on your needs, you can choose to configure your firewall either as a whitelist or a blacklist model. In the case with the former, only web traffic that complies with certain criteria can pass.
The latter, on the contrary, excludes certain traffic from entering your website.
Note: Romexsoft has experience configuring WAF solutions to help organizations meet PCI-DSS and HIPAA compliance requirements.
To sum up, to ensure that your web app development project goes smooth you’ll need to decide on:
- The right tech stack and web development framework;
- Determine the most suitable web application life cycle model;
- Map out a strong web development process;
- Consider the application security requirements;
- Decide on the basics of web design and UX.
And if you need help at any of those stages, don’t hesitate to get in touch with the Romexsoft team. We can help you assemble a dedicated development team for your enterprise web app development project, and/or provide ad hoc AWS consulting.
Enterprise Web Application FAQ
An enterprise web application is a custom-built software solution designed specifically for the internal or external operations of a single enterprise. It is usually tailored to meet the unique workflows, integrations, security requirements, and data management needs of that specific organization. Enterprise web apps can be hosted on-premises, in the cloud, or as part of a hybrid infrastructure, and access is typically restricted to authorized users within the company or its ecosystem.
In contrast, an enterprise SaaS (Software-as-a-Service) platform is a multi-tenant, cloud-based solution built to serve many enterprise customers simultaneously. SaaS platforms are typically developed by software vendors and offered as subscription services. While they may allow configuration and integrations, they are not custom-built for each enterprise. Examples include Salesforce, HubSpot, and ServiceNow.
Yes, enterprise web applications are ideal for building systems that manage complex business functions like supply chain, HR, and CRM. These apps enable real-time data access, process automation, and integration with existing enterprise systems.
Common use cases include:
Supply Chain: inventory tracking, logistics, vendor portals
HR: onboarding, payroll, performance management
CRM: lead tracking, customer service, marketing automation
Yes, migrating a legacy system to a modern enterprise web application is entirely possible and often recommended. The process involves evaluating the existing system, re-engineering outdated components, modernizing the user interface, and integrating new technologies to ensure better scalability, performance, and security. This kind of migration helps businesses reduce technical debt, improve maintainability, and align the system with current operational and user needs.
The cost of developing a web application varies significantly based on the project’s complexity, required features, development team size, and the vendor’s location and experience. For most enterprise-grade web apps developed by a mid-sized agency, the average cost falls between $200K and $700K, with ongoing maintenance adding another 15–25% annually.



